Employers today face any number of scheduling challenges – talent shortages, supply chain disruptions, fluctuating consumer demand and employee preferences for greater flexibility. To overcome these obstacles, they must consider innovative approaches to shift planning1, like collaborative scheduling and new forms of scheduling technology. Solutions with forecasting algorithms and artificial intelligence can help maintain productivity even if unforeseen circumstances arise.
Table of Contents
What is shift planning?
Shift planning is the process of assigning employees to work during busy business hours and scaling back staff when consumer demand subsides. In this way, employers help ensure they have the right people working at the right times to maximize workforce productivity and minimize costs.
Yet, the needs of the company should not outweigh the needs of the employees. There is a human element to shift planning and if employers want to keep employees engaged and retain their services, they must prioritize work-life balance.
One way to take a more employee-centered approach to shift planning is to embrace collaborative scheduling. Instead of managers creating schedules alone, they allow employees to pre-set their preferences and availability, or swap shifts with their colleagues. With this increased control, employees tend to be absent less and experience better job satisfaction.
How to get started with shift planning
Collaborative scheduling and other modern approaches to shift planning require technology. To successfully transition from manual processes to a software solution, employers typically follow these steps:
- Evaluate the organization’s needs and consult with employee scheduling software providers to see if their features meet the business requirements.
- Test the selected software with a small team and make any necessary adjustments based on their feedback.
- Roll out the scheduling platform to the rest of the organization, along with focused employee education and training sessions.
- Providing ongoing support so employees can easily review their schedules and managers can approve schedule requests.
- Create a scheduling policy that is widely communicated to employees and introduced to new hires during onboarding.
- Conduct regular workforce analysis to ensure that scheduled labor levels are consistent with the organization’s goals and growth objectives.
Shift planning best practices
A scheduling solution that helps prevent understaffing and overstaffing while balancing the needs of the employer and the employee may be considered the gold standard in shift planning. Even with the right tools, employers can still benefit from some basic best practices:
- Ensure that each shift has workers with the requisite skillsets to meet business demands.
- Make schedules easy to access and publish them at least two weeks in advance.2
- Be transparent with employees and explain how scheduling decisions are made.
- Comply with the applicable laws governing predictive scheduling, overtime, meal breaks, shift length, etc.
- Expect changes and have replacements ready if someone unexpectedly calls out sick.
Benefits of shift planning
Shift planning software gives supervisors more visibility into schedules, empowers employees to take more control over their work structure and increases communication among all parties. In turn, employers may be able to:
- Deliver exceptional customer experiences across all channels.
- Maximize productivity in all locations and control costs.
- Keep pace with evolving market conditions.
- Improve strategic planning and conversion rates.
- Engage and retain valued employees.
How to calculate shift planning costs
With the right workforce management solution, employers have greater control of their labor costs. They can:
- Use metrics, such as hours worked and labor constraints, to calculate shift planning expenses.
- View labor forecasts, budgets, and actual costs to plan schedules more effectively for a location.
- Adjust schedules in real time to meet business demands while staying within budgets.
Shift planning example
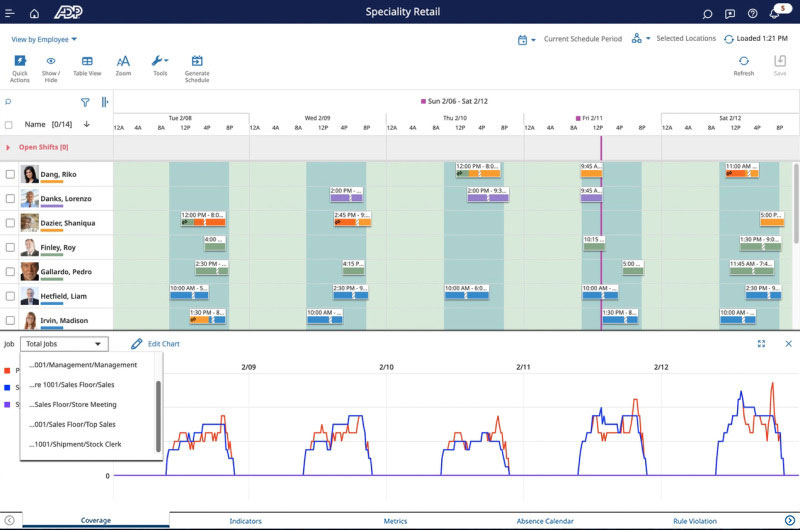
In this example, an employer uses a workforce management solution with optimized scheduling and forecasting. It is capable of:
- Forecasting labor needs and creating schedules that minimize costs and maximize productivity.
- Automating forecasting, increasing accuracy down to 15-minute increments to meet employer, business, and budget requirements.
- Providing at-a-glance views of business performance information that can be filtered to specific locations.
Best shift planning software features
There are multiple levels of shift planning solutions, ranging from basic online scheduling to more advanced, system-assisted scheduling. Depending on their specific needs and the solution they choose, employers can expect to:
- Easily plan, build, and manage schedules from a smartphone or tablet.
- Improve the decision-making process with the aid of AI recommendations.
- Predict labor needs accurately using precise business and labor forecasting algorithms and actionable data.
- Ensure appropriately skilled employees are scheduled when they are needed most.
- Empower employees and prioritize their preferences with self-scheduling, shift swaps and last-minute changes.
- Access up-to-the-minute scheduling data to help stay on budget.
- Set, monitor, and report on workforce key performance indicators (KPIs), including efficiency, productivity, forecasting accuracy, labor utilization and other custom KPIs.
Frequently asked questions about how to schedule shifts
Why is shift planning important?
Shift planning is essential because understaffing and overstaffing increase labor costs. Mismanaged schedules can also lead to disengaged employees, poor productivity, and higher turnover rates.
What should be included in a shift planner?
At the very least, a shift planner should offer online and mobile scheduling capabilities and some form of employee self-service. More advanced solutions may provide collaborative scheduling, business and labor forecasting, and access to real-time, actionable data.
What is shift-based HR planning?
Shift-based HR planning strives to coordinate the number of employees working at any given time with the expected consumer or business demand. The goal is to prevent understaffing and overstaffing, both of which increase labor costs.
What are five scheduling principles?
- Align schedules to fluctuating business demands to reduce overtime and labor costs.
- Incorporate employee preferences when scheduling shifts to avoid dissatisfaction and burnout.
- Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), such as efficiency, productivity, labor utilization, etc.
- Address differing labor requirements in each location to improve service and conversion rates.
- Comply with regulations concerning overtime, shift breaks and fair scheduling, as well as predictive scheduling laws where applicable.
What are common work schedules?
There is a shift schedule to fit almost any business or industry need. Examples include:
- Fixed schedule – Employees work the same hours from one week to the next.
- Split schedule – Employees work two non-consecutive shifts on the same day.
- Rotating schedule – Employees work different shifts from week to week.
- Flex schedule – Employees make their own hours within certain limits.
- Compressed schedule – Employees put in an entire week’s worth of work in fewer days.
- On-call schedule – Employees work during off-business hours only when needed.
This article is intended to be used as a starting point in analyzing how to make work schedules and is not a comprehensive resource of requirements. It offers practical information concerning the subject matter and is provided with the understanding that ADP is not rendering legal or tax advice or other professional services.
1This article is not meant to encompass predictive scheduling law requirements or compliance with the same.
2Note that predictive scheduling laws, if applicable, may impact creation of schedules, when and how they are provided to employees and other factors.




